-
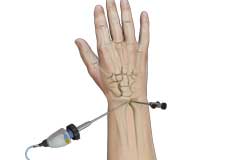
Wrist Arthroscopy
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to view, diagnose and treat problems of your wrist joint.
-
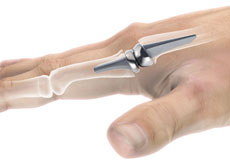
Wrist Joint Replacement
The wrist is a complex joint made up of 8 carpal bones aligned in two rows with four bones present in each row. The carpal bones are further connected to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each small bone forms a joint with the bone next to it.
-
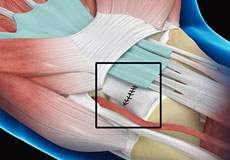
Wrist Ligament Reconstruction
Ligament reconstruction procedure can be performed as day surgery under local or general anesthesia.
-
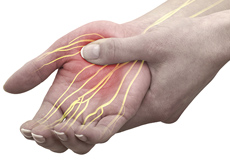
Peripheral Nerve Repair
The peripheral nerves are the nerve fibers that compose the area from head to toe, connecting the brain and spinal cord with the rest of the body parts. Nerves transmit electrical impulses and signals to and from the brain
-
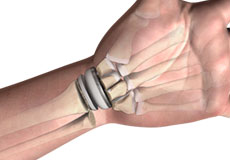
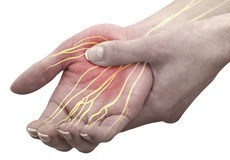
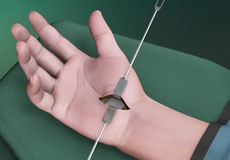
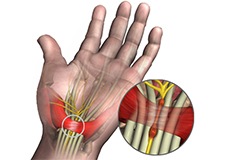
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by the compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.
-
Elective Emergency Hand Surgery
Hand surgery is performed to restore the structure and functionality of the fingers, wrist and hand secondary to a traumatic injury, medical condition, severe infection, or birth defect causing pain and/or deformity of the hand.
-
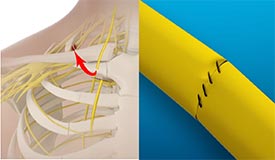
Nerve Transfers
A nerve transfer is a surgical procedure in which a portion of a healthy nerve is transferred to the site of a damaged nerve. This procedure is performed to restore normal function at the injured site.
-
Microvascular Surgery
Microvascular surgery or microsurgery is a surgical technique for joining or repairing the damaged blood vessels and nerves during reconstructive surgery of body parts. Reconstructive surgery restores the functioning of the body parts by improving circulation.
-
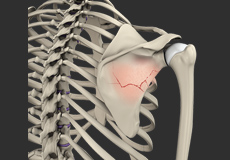
Total Wrist Arthrodesis
Arthrodesis is the surgical immobilization of a joint by the fusion of the adjacent bones.
-
Hand Fracture Surgery
The hand is one of the most flexible and useful parts of our body. Because of overuse in various activities, the hands are more prone to injuries, such as sprains and strains, fractures and dislocations, lacerations and amputations while operating machinery, bracing against a fall and sports-related injuries.
-
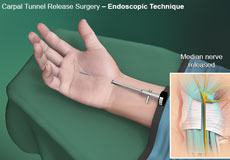
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Surgery
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway on the palm side of your wrist. Small wrist bones known as carpals form the bottom and sides of the carpal tunnel and a strong band of connecting tissue, known as the transverse carpal ligament, covers the top of the carpal tunnel.
-
Wrist Fracture Fixation
Wrist fractures are breaks in any of the bones that form your wrist joint.
-
Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.
-
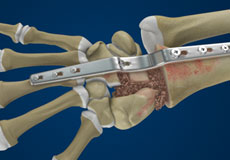
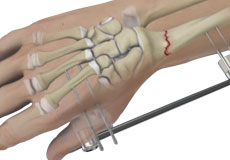
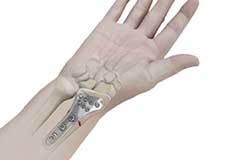
Wrist Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
Open reduction and internal fixation of the wrist is a surgical technique employed for the treatment of severe wrist fractures to restore normal anatomy and improve range of motion and function.
-
Sports Injury Management of Hand, Wrist and Elbow
Sports injuries are injuries that most commonly occur during sports and exercises. These injuries may result from accidents, poor training practices, and use of improper protective gear, lack of conditioning, and insufficient warm-up and stretching.
-
Surgery for Thumb and Digit Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis; the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis that affects the joint at the base of the thumb.
-
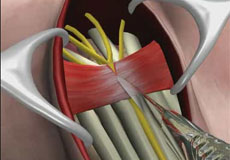
Nerve Decompression of the Upper Extremities
Nerve decompression of the upper extremities, also called peripheral nerve decompression, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure employed to relieve pressure on an entrapped or pinched nerve (neuroma) for the treatment of conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome, the two most common nerve compression syndromes.
-
Distal Radioulnar Joint Arthroscopy
The distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) is a pivot type synovial joint located between the radius and the ulna just proximal to the wrist joint and assists in pronation and supination of the forearm.
-
Ulnar Nerve Compression in Guyon's Canal
Ulnar nerve compression in Guyon’s canal is a condition characterized by pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling sensation in the hand. The condition occurs when the ulnar nerve, the nerve that travels across the elbow from the shoulder to the hand, is compressed as it goes from the wrist into the hand through a space known as Guyon’s canal.
-
Extensor Tendon Injuries
Tendons are bands of tissue connecting muscles to bones. The extensor tendon is a strong, smooth cord that connects finger bones to muscles in the hand. Extensor tendons are located just under the skin, directly on the bone, on the back of the hand and fingers.
-
Nerve Lacerations
Coming soon
-
Wrist Fracture
The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm. The bones meet to form multiple large and small joints. A wrist fracture refers to a break in one or more of these bones.
-
Fractures of the Hand and Fingers
A finger fracture is not a minor injury, and if left untreated, can lead to stiffness, pain, disruption of the alignment of the whole hand and interference with specialized functions such as grasping or manipulating objects.
-
Thumb Fracture
A break or a crack in the bones of the thumb is known as a thumb fracture. Fractures may occur anywhere on the thumb, but a fracture at the base of the thumb, near the wrist, is considered the most serious.
-
Scaphoid Fracture
Scaphoid fracture occurs due to a fall on an outstretched hand with complete weight falling on the palm. This fracture usually occurs during motor accidents or sports activities.
-
Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis and the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis. Arthritis affects various joints in the body and the arthritis in the hand affects the joint at the base of the thumb. Arthritis may also affect the joints of other digits.
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.
-
De Quervain's Tendinosis
Inflammation and swelling of the tendon sheaths put pressure on the adjacent nerves and leads to pain and numbness in the thumb side of the wrist. Strain on these tendons can cause swelling and irritation, and lead to a condition called De Quervain's tenosynovitis, which is characterized by inflammation.
-
Dupuytren's Contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is a hand condition where thickening of the underlying fibrous tissues of the palm causes the fingers to bend inward. This makes it difficult to fully straighten the affected fingers.
-
Trigger Finger
Inflammation in the tenosynovium leads to a condition called trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis or flexor tendonitis, where one of the fingers or thumb of the hand is caught in a bent position.
-
Wrist Injuries
The wrist is a commonly injured joint in the body. Problems include sprains and strains as well as fractures that can occur with lifting and carrying heavy objects, while operating machinery, bracing against a fall, or from sports-related injuries.
-
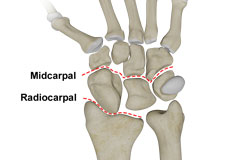
Carpal Instability
Carpal instability is the loss of alignment of the carpal bones and/or radioulnar joint. The wrist is a complex joint that connects the forearm to the hand and allows it to move. It consists of 8 small bones called carpals that articulate with two long bones of the forearm (radius and ulna).
-
Wrist Pain
Wrist pain is defined as any ache or discomfort in the wrist. The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm. The bones meet to form multiple large and small joints. A trauma or injury to one or more of these bones results in wrist pain.
-
Wrist Sprain
Injuries caused due to stretching or tearing of the ligaments in the wrist are called wrist sprains. Sprains can range from mild to severe, based on the extent of injury to the ligament.
-
Wrist Ligament Tear and Instability
A ligament is a strong, flexible band of fibrous tissue. The wrist has many ligaments that help to keep the wrist bones in proper position providing stability to the joint. A torn ligament causes the wrist bones to move out of their position, which in turn leads to wrist instability as the sprained (torn) ligament can no longer support the wrist bones.
-
Brachial Plexus Injury
A brachial plexus injury is a condition characterized by injury or damage to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that emerges from the spinal cord in the neck region. The brachial plexus enables the movement of the muscles in the arms and shoulders and sensation in the overlying skin.
-
Finger Joint Dislocation and Volar Plate Injury
Finger dislocation is a condition where the bones of your finger have moved away from its normal anatomical position.
-
Distal Intersection Syndrome
Distal intersection syndrome also referred to as tenosynovitis of the radial wrist extensors is characterized by the radial wrist and forearm pain. Distal intersection syndrome is tenosynovitis of the third extensor compartment (extensor pollicis longus) where it crosses the second extensor compartment.
-
Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts are swellings that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of wrists or hands. They can be found either at the top of the wrist, palm side of the wrist, end joint of a finger or at the base of a finger. A ganglion cyst is not cancerous and will not spread to the other parts of the body.
-
Hand Pain
Hand pain is characterized by distress in the joints and tissues of the hand or fingers. Hand pain can be depicted as pulsating, aching, increased warmth, prickling, irritation and inflexibility.
-
Hand Infections
Hand infections, if left untreated or treated improperly, can cause disabilities such as stiffness, contracture, weakness, and loss of tissues (skin, nerve and bone) that will persist even after the infection resolves. Therefore, prompt treatment of hand infections is important.
-
Wrist Tumors
A tumor is a lump or abnormal growth formed due to unregulated cell division. Wrist tumors can occur on or underneath the skin. They are most often benign (non-cancerous).
-
Gamekeeper's Thumb
Gamekeeper's thumb, also known as skier's thumb, is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament, a band of tissue that supports the joint at the base of the thumb.
-
Skier's Thumb
Skier's thumb, also known as, Gamekeeper's thumb is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament, a band of tissue that supports the joint at the base of the thumb. Damage to the ulnar collateral ligament may lead to chronic instability of the thumb, creating problems in its normal functioning.
-
Boxer's Fracture
A boxer’s fracture is a break in the neck of the fifth metacarpal bone of the hand (below the pinky finger) close to the knuckle. The hand is composed of 3 types of bones: carpal or wrist bones, metacarpals or long hand bones, and phalanges or finger bones.
-
Bennett's Fracture
Bennet’s fracture is a break at the base of the first metacarpal bone (thumb bone) that meets the wrist at the first carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. The hand is composed of 3 types of bones: carpals or wrist bones, metacarpals or long hand bones, and phalanges or finger bones. Metacarpals consist of five long bones that connect the carpals with the phalanges.
-
Kienbock's Disease
Kienbock's disease is a condition in which the lunate, one of the small bones of the wrist loses its blood supply leading to death of the bone. This results in pain, stiffness, and degenerative changes in the wrist joint.
-
Ulnar Carpal Impaction
The wrist is a complex joint made up of 8 carpal bones aligned in two rows, with four bones present in each row. The carpal bones are further connected to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each small bone forms a joint with the bone next to it.
-
Hand Tumors
Any abnormal lump or bump on the hand is considered a hand tumor. Hand tumors can occur on the skin as a mole or a wart, underneath the skin soft tissue or on the bone. Most hand tumors are benign (non-cancerous); however, they can also rarely be malignant (cancerous).
-
Fingertip Injuries
A fingertip injury is a wound or damage caused to the most distal portion of the finger. It can be a crush, a sharp cut, a tear or a combination of these, and can result in damage to the skin, nail or nailbed, tendon, pulp, bone, and nerve endings.
-
Malunion of a Fracture
Malunion of a fracture is a condition where the fractured ends of a bone heal in a misaligned position resulting in bone deformity. Malunions may occur in any bone fractures in the body often due to trauma.
-
Hand Therapy
Hand therapy is a rehabilitation technique recommended to improve the strength and restore functional activity of hands in patients with upper extremity injuries. Hand therapy also helps in preventing injury.
-
Distal Radioulnar Joint (DRUJ) Instability
The distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) is a pivot type synovial joint located between the radius and the ulna just proximal to the wrist joint and assists in pronation and supination of the forearm.
-
Work Related Hand Injuries
The hand is one of the most flexible and useful parts of our body that assist us in most workplace activities. Hand injuries can range from minor cuts or burns to severe injuries.
-
Non-Surgical Treatment of Hand and Wrist
The hand is one of the most flexible and useful parts of our body that enable us to perform many of our daily activities. The hands and wrists are prone to injuries or certain orthopedic conditions and can range from minor cuts or burns to severe arthritis or injuries of nerves, bones, and tendons.
Hand Anatomy
The human hand is made up of the wrist, palm, and fingers and consists of 27 bones, 27 joints, 34 muscles, over 100 ligaments and tendons, and many blood vessels and nerves.
The hands enable us to perform many of our daily activities such as driving, writing and cooking. It is important to understand the normal anatomy of the hand to learn more about diseases and conditions that can affect our hands.
Bones of the Hand
The wrist is comprised of 8 carpal bones. These wrist bones are attached to the radius and ulna of the forearm to form the wrist joint. They connect to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each metacarpal bone connects to one finger at a joint called the metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP joint). This joint is commonly referred to as the knuckle joint.
The bones in our fingers and thumb are called phalanges. Each finger has 3 phalanges separated by two interphalangeal joints, except for the thumb, which has only 2 phalanges and one interphalangeal joint.
The first joint close to the knuckle joint is called the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP joint). The joint closest to the end of the finger is called the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint).
The MCP and PIP joint act like hinges when the fingers bend and straighten.
Soft Tissues of the Hand
Our hand bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues. These include: articular cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons.
Articular cartilages are smooth material that act as shock absorbers and cushion the ends of bones at each of the 27 joints, allowing smooth movement of the hand.
Muscles and ligaments function to control the movement of the hand.
Ligaments are tough rope-like tissues that connect bones to other bones, holding them in place and providing stability to the joints. Each finger joint has two collateral ligaments on either side, which prevents the abnormal sideways bending of the joints. The volar plate is the strongest ligament in the hand. It joins the proximal and middle phalanx on the palm side of the joint and prevents backward bending of the PIP joint (hyperextension).
Muscles of the Hand
Muscles are fibrous tissues that help produce movement. They work by contracting.
There are two types of muscles in the hand:
- Intrinsic muscles are small muscles that originate in the wrist and hand. They are responsible for fine motor movements of the fingers during activities such as writing or playing the piano.
- Extrinsic muscles that originate in the forearm or elbow control the movement of the wrist and hand. These muscles are responsible for gross hand movements. They position the wrist and hand while the fingers perform fine motor movements.
Each finger has six muscles controlling its movement: three extrinsic and three intrinsic muscles. The index and little finger each have an extra extrinsic extensor.
Tendons of the Hand
Tendons are soft tissues that connect muscles to bones. When muscles contract, tendons pull the bones, causing the finger to move. The extrinsic muscles are attached to finger bones through long tendons that extend from the forearm through the wrist. Tendons located on the palm side help in bending the fingers and are called flexor tendons, while tendons on top of the hand called extensor tendons help in straightening the fingers.
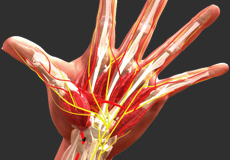
Nerves of the Hand
Nerves of the hand carry electrical signals from the brain to the muscles in the forearm and hand, enabling movement. They also carry the senses of touch, pain and temperature back from the hands to the brain.
The three main nerves of the hand and wrist include:
- Ulnar nerve: The ulnar nerve crosses the wrist through an area called Guyon’s canal and branches to provide sensation to the little finger and half of the ring finger.
- Median nerve: The median nerve crosses the wrist through a tunnel called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve provides sensation to the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger and part of the ring finger.
- Radial nerve: The radial nerve runs down the thumb side of the forearm and provides sensation to the back of the hand from the thumb to the middle finger.
All three nerves originate at the shoulder and travel down the arm to the hand. Each of these nerves has sensory and motor components.
Blood Vessels of the Hand
Blood vessels travel beside the nerves to supply blood to the hand. The main arteries are the ulnar and radial arteries, which supply blood to the front of the hand, fingers, and thumb. The ulnar artery travels next to the ulnar nerve through the Guyon’s canal in the wrist. The radial artery is the largest artery of the hand, traveling across the front of the wrist, near the thumb. Pulse is measured at the radial artery.
Other blood vessels travel across the back of the wrist to supply blood to the back of the hand, fingers and thumb.
Bursae of the Hand
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that decrease friction between tendons and bone or skin. They contain special cells called synovial cells that secrete a lubricating fluid.